Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. In fact, one in three adults will develop gum disease at some point in their lifetime. Furthermore, your risk of developing gum disease increases with age.
While early stages of gum disease can often be managed with proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits, advanced gum disease requires more intensive treatment. It can also have serious consequences for your oral health.
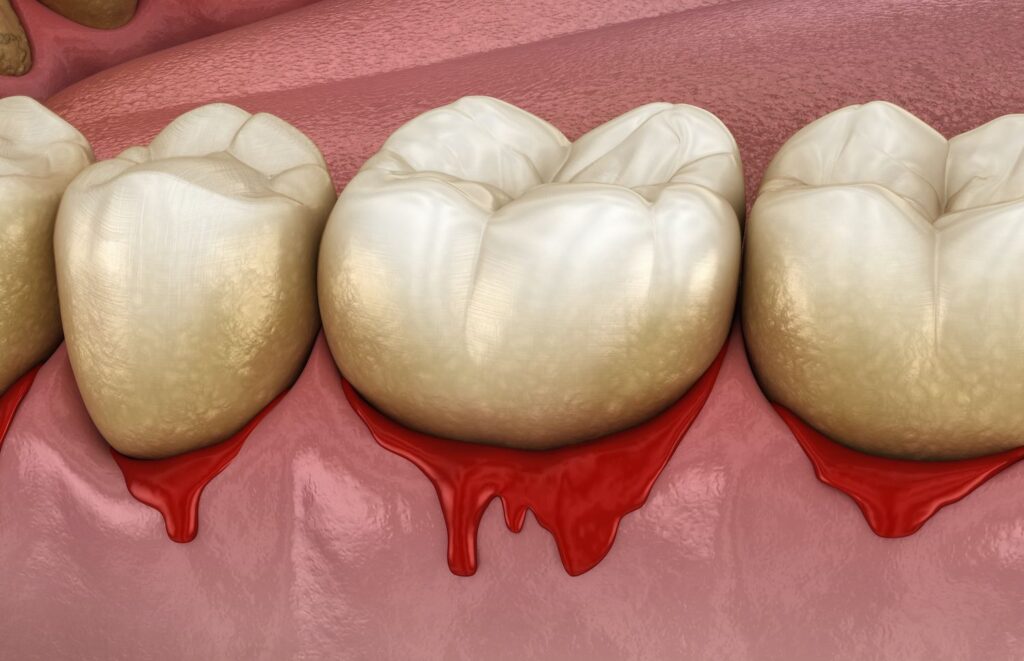
What is Advanced Gum Disease?
Advanced gum disease, also known as periodontitis, occurs when the bacterial infection in the gums spreads beyond the gum line. Then, it begins to affect the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone and ligaments. This can lead to major damage to the tissues that hold your teeth in place. Eventually, this can result in tooth loss if left untreated.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of advanced gum disease is crucial for seeking prompt treatment. Some common symptoms include:
Gum Recession: As the gums pull away from the teeth, you may notice that your teeth appear longer than before.
Deep Pockets: Healthy gums fit snugly around the teeth, but in advanced gum disease, pockets form between the gums and teeth, often measuring five millimeters or more.
Gum Bleeding: Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing, can indicate inflammation and infection.
Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath, or halitosis, is often a result of the bacteria that thrive in the pockets formed by advanced gum disease.
Loose Teeth: As the supporting structures weaken, you may notice that your teeth feel loose or shift out of place.
Side Effects of Gum Disease
Ignoring advanced gum disease can cause serious issues for your oral health and overall well-being. Some potential complications include:
The destruction of the bone and ligaments that support the teeth can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Additionally, this can affect your ability to chew and speak properly. Advanced gum disease can also cause the bone surrounding the teeth to break down. This can lead to changes in facial structure and an aged appearance.
Research has linked advanced gum disease to an increased risk of other systemic health issues, including heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Furthermore, the inflammation with advanced gum disease can worsen existing inflammatory conditions throughout the body, such as arthritis.
Treatment Options
Fortunately, there are effective treatments available for advanced gum disease. Your dentist may recommend one or more of the following:
Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smooths the tooth roots to promote healing.
Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control the bacterial infection and reduce inflammation.
Surgery: In advanced cases where nonsurgical treatments are not sufficient, surgical interventions such as flap surgery or bone grafting may be necessary to restore oral health.
Finally, improving oral hygiene habits, quitting smoking, and managing underlying health conditions can all contribute to better outcomes for advanced gum disease treatment.
